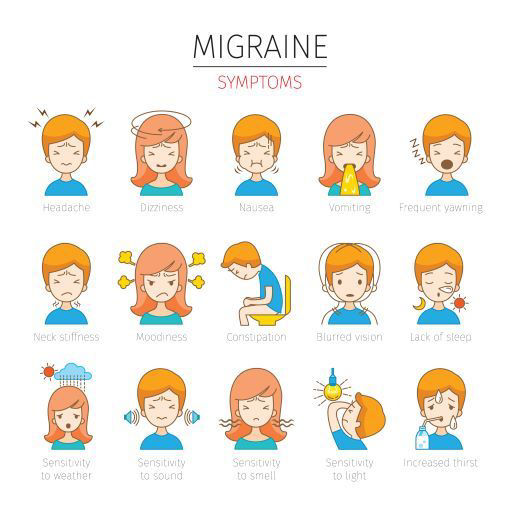
-
How long do migraines last?
If left untreated, a migraine often lasts 4 to 72 hours. Each person experiences migraines differently. Migraines can hit infrequently or repeatedly each month.
-
What triggers migraines?
Being hungry or thirsty, experiencing stress, or changes in routine are all common migraine triggers. Keeping a migraine journal can assist you in identifying your triggers because there are so many potential triggers.
-
Can stress cause migraines?
Migraines and headaches of the tension type are frequently brought on by stress. Other sorts of headaches may also be brought on by it or made worse by it. Children and young people are more likely than adults to experience headaches when under stress.
-
Can migraines cause dizziness?
Migraine-related vertigo can take many distinct forms. Patients may experience vertigo, just feel dizzy and unstable, or think that something is off with their head. These sensations can last a few seconds, a few minutes, an hour, or even a few days, and they can happen singly or in combination.
-
Can migraines cause fever?
In addition to other serious symptoms, occasional hemiplegic migraines can cause severe episodes that include fever. Fever is a migraine symptom, but only during really severe episodes, just like in familial hemiplegic migraines.
-
Can anxiety cause migraines?
Migraines can be brought on by panic episodes and anxious feelings. For instance, if anxiety prevents you from getting enough sleep, you can start to worry more and more about how you'll manage without sleep. A migraine may develop as a result of this increased worry.
-
Can high blood pressure cause migraines?
According to several studies, migraines are inversely correlated with lower systolic but higher diastolic blood pressure. In fact, a connection between migraines and low blood pressure has been discovered in certain research. People who have uncontrolled chronic high blood pressure appear to get migraines more frequently.
-
Can dehydration cause migraines?
A dehydrated person is more susceptible to heat exhaustion and other types of heat disease. Dehydration can trigger (cause) a migraine headache. Water consumption is crucial if you suffer from migraines. You might be able to avoid a migraine attack by staying hydrated.
-
What foods triggers Migraine?
Every person has a different trigger for Migraines. However, those who suffer from frequent Migraine attacks are advised to avoid caffeine, aged cheeses, processed meat, alcohol, MSG, citrus fruits, chocolates, spicy foods, and any food containing aspartame.
-
What should I eat if I have a Migraine?
If you have Migraines then it is advisable to stick to foods that can help prevent headaches. Such as:
- Orange, yellow, and green vegetables, such as summer squash, sweet potatoes, carrots, and spinach
- Carbonated, spring, or tap water
- Rice, especially brown rice
- Dried or cooked fruits, particularly non-citrus kinds such as cherries and cranberries
- Natural sweeteners or flavors, such as maple syrup and vanilla extract
-
Where do Migraines hurt?
Migraines are severe headaches usually described as throbbing or pulsating pain on one side or both sides of the head.
-
What is stomach migraine?
Migraines in children are usually centered on digestive issues and maybe relieved after throwing up or the migraines accompanied by diarrhea. These are known as stomach migraines.
-
Should you lay down with a Migraine?
Yes. Whenever possible, lie down in a dark and quiet place until the pain passes. This will help reduce the Migraine intensity and help you relax. Sometimes it also helps to keep a damp cloth on your forehead or give yourself a scalp massage.
-
Are migraines a disability?
Migraines are ranked as the ninth most common cause of disability worldwide by the World Health Organization.
-
Are migraines hereditary?
An important factor in migraine is genetics. This indicates that it frequently runs in families. According to estimates, genes account for up to 60% of migraine sufferers. People with these genes are more susceptible to environmental changes, such as alterations in lifestyle and potential attack triggers.
-
Is migraine dangerous?
Even though Migraines are painful and affect the quality of life, they are not otherwise dangerous. Several studies have revealed that those suffering from migraines with aura are at a high risk of ischemic stroke.
-
Is coffee good for Migraines?
No. It is best to avoid caffeinated drinks such as coffee if you suffer from Migraines.
-
When should I go to the hospital for a Migraine?
If you are suffering from a Migraine, you should see a doctor if:
- This is your first Migraine attack
- Your Migraine symptoms are worse than usual
- You have visual disturbances or loss of senses or speech slurring
- Your Migraine attacks are more frequent than once a week
-
What does a migraine feel like?
After a Migraine attack, you may feel fatigued, sensitivity to bright lights, loud sound, low energy, and depression. Some people also experience an inability to focus on daily tasks described as a ‘mental fog’.
-
Why does throwing up relieve Migraines?
Throwing up may end the Migraine for some people, while others experience vomiting as an accompanying feature of Migraine headaches. There is no definite explanation for why vomiting may relieve Migraine headaches.
Some researchers believe that vomiting marks the normalization of gut movement that is hindered by the Migraine. That is why the end of the Migraine is marked by vomiting and some people also experience relief in their Migraine headache by inducing vomiting.
-
Can migraines make you poop?
Migraines trigger different body reactions from different people. Some people get diarrhea as an accompanying symptom of Migraines. There is no definite medical explanation for why this happens.
-
How to sleep with a migraine?
It is usually recommended that people with Migraines should sleep in a dark, quiet room to relieve their headache. Sometimes it also helps to keep a damp cloth on your forehead or give yourself a scalp massage.
-
What is a silent Migraine?
A silent Migraine is when you experience the ‘aura’ that sometimes accompanies the headache in a Migraine, but you don’t feel any pain.
-
What are the pressure points to relieve Migraines?
Acupressure experts say that it is possible to relieve a Migraine headache by applying pressure to a point called ‘Hegu’ or the point between the base of your thumb and index finger.
-
Can you wake up with a migraine?
Some reasons why you wake up with a Migraine could be dehydration, poor sleeping habits, disturbed sleep, stress, or side effects of medication.
-
Can Migraines cause long term damage?
Yes. Research has proved that frequent Migraine attacks cause damage to the brain structure in the long term. It increases the risk of lesions, stroke, and may harm the nervous system.
-
Do Migraines get worse with age?
Migraines are usually worse in adulthood. People between the ages of 35 to 45 report the highest intensity and duration of Migraine attacks.
-
Do Migraines affect memory?
No. There is no medical evidence to suggest that Migraines can affect the memory of the individual.
-
Do Migraines show up on an MRI?
No, Migraines cannot be diagnosed in an MRI scan. However, an MRI scan helps the doctors in ruling out other medical conditions that may cause headaches such as infections, fluid buildup, and tumors.
-
What are some effective home remedies for migraines?
Home remedies for migraine include:
- Avoid foods that trigger migraines such as caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods, etc.
- Inhale lavender oils during a migraine attack
- Acupressure on the point near the base of your thumb and index finger
- Follow a healthy lifestyle
- Include magnesium-rich foods in your diet